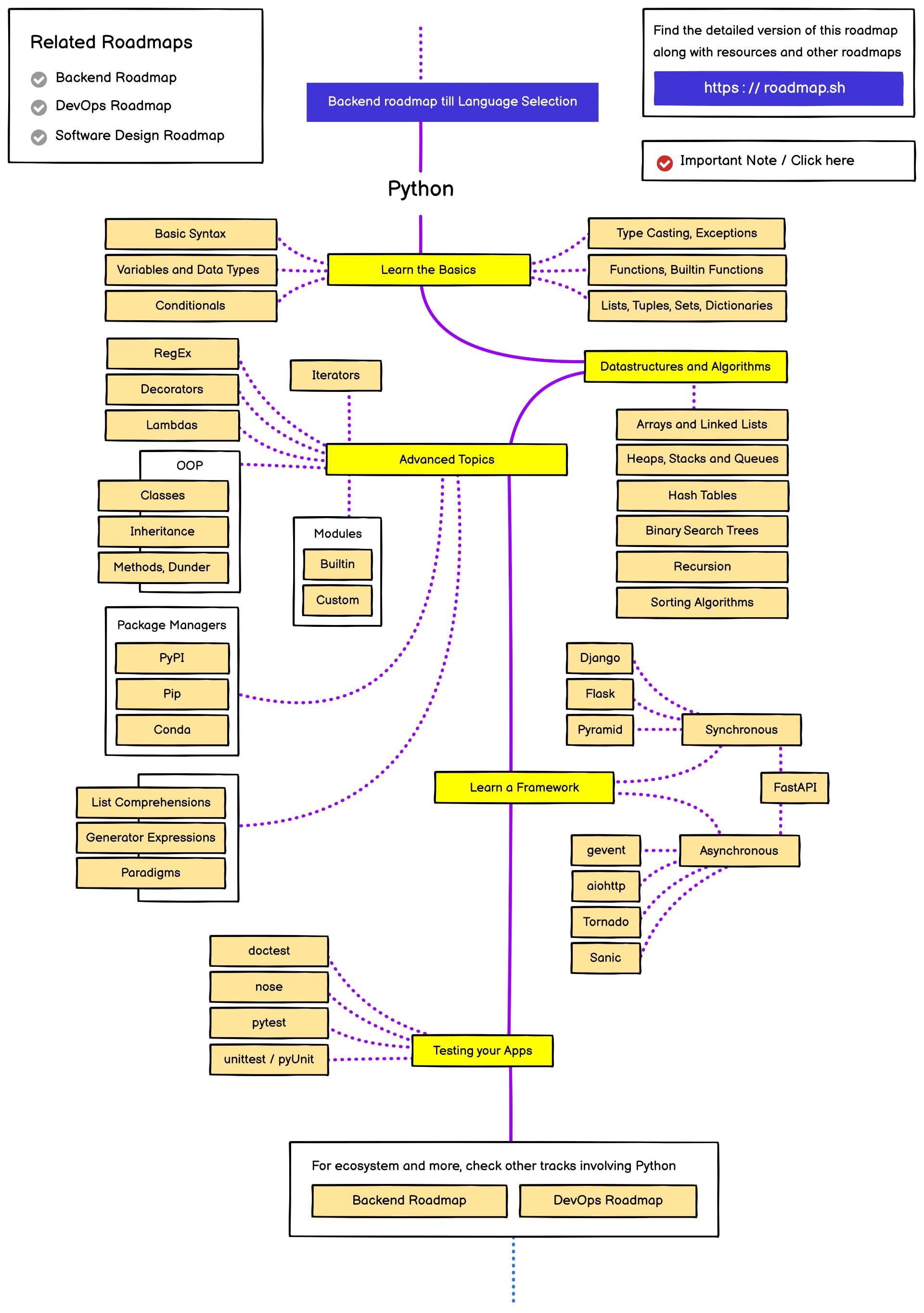
Python
introduction
Python, pronounced /ˈpaɪθən/ in British English and /ˈpaɪθɑːn/ in American English, is a computer programming language developed by Dutch scientist Guido van Rossum during the year 1989. In the Python language, everything is an object, including functions, which also possess their own attributes. Python is an interpreted programming language, and when running Python programs, it is necessary to have the interpreter translate the Python code.
Python is an unrestricted, cross-platform open-source programming language known for its fast data processing speed, powerful features, and ease of learning, making it widely used in data analysis and processing. Furthermore, Python operates in an interpreted manner, allowing code to be executed directly through the interpreter without the need for compilation, which is characteristic of dynamic languages and results in high programming efficiency. Python is a fully object-oriented language, where numbers, modules, strings, and data structures are all objects, and it supports common class concepts such as inheritance, overloading, derivation, and multiple inheritance.
On July 20, 2017, IEEE released the 2017 programming language rankings, with Python ranking first. In March 2018, the language's author announced on a mailing list that support for Python 2.7 would end on January 1, 2020. Users wishing to continue receiving support related to Python 2.7 after this date would need to pay commercial vendors for assistance.
roadmap: